asynchronous I/O #
首先给出synchronous IO和asynchronous IO的定义:
- A synchronous I/O operation causes the requesting process to be blocked until that I/O operation completes;
- An asynchronous I/O operation does not cause the requesting process to be blocked;
两者的区别就在于synchronous IO做”IO operation”的时候会将进程阻塞。
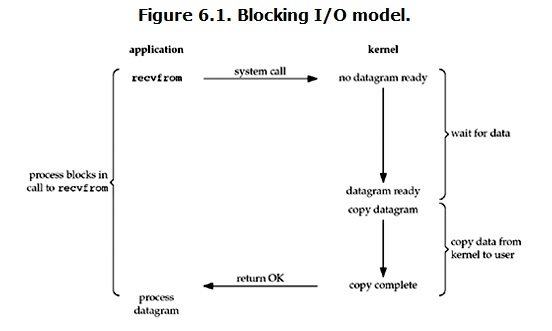
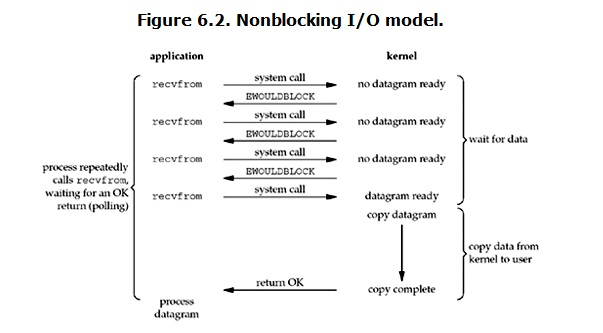
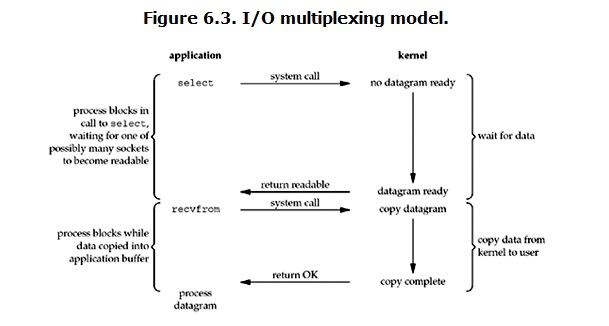
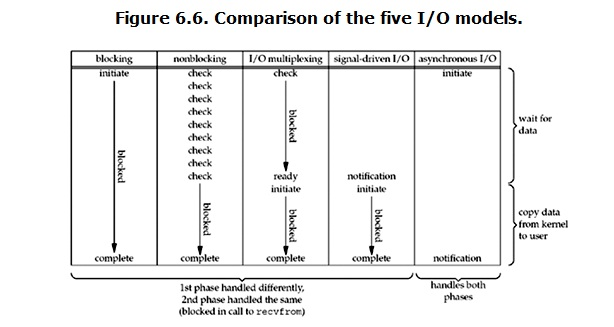
之前所述的blocking IO,non-blocking IO,IO multiplexing都属于synchronous IO。
定义中所指的”IO operation”是指真实的IO操作,如下图例子中的recvfrom这个system call。non-blocking IO在执行recvfrom这个system call的时候,如果kernel的数据没有准备好,这时候不会block进程。但是,当kernel中数据准备好的时候,recvfrom会将数据从kernel拷贝到用户内存中,这个时候进程还是被block了的。
而asynchronous IO则不一样,当进程发起IO 操作之后,就直接返回再也不理睬了,直到kernel发送一个信号,告诉进程说IO完成。在这整个过程中,进程完全没有被block。
Linux下的asynchronous I/O其实用得很少,epoll + O_NONBLOCK 已经能解决大部分问题了
在理想的异步环境下,数据准备阶段和数据拷贝阶段都是由内核完成的,不会对用户线程进行阻塞,这种内核级别的改进自然需要操作系统底层的功能支持。
POSIX AIO(aio_read / aio_write)是标准,不是实现。Linux下的POSIX AIO实现由 glibc 在 user space 用多线程+同步阻塞 IO 模拟的,效率还远不如 epoll。大致过程如下:
- aio_read() 只是登记请求,请求塞进一个全局AIO队列
- 线程池中唤醒/分配一个工作线程,阻塞 read/write,线程会被卡住,直到 I/O 完成
- I/O完成后按照指定的方式通知,信号或者回调函数等
libaio是Linux 内核 AIO,io_submit,并不兼容POSIX AIO,不支持socket主要针对数据库,如MySQL
io_uring是现代 Linux 异步 I/O,模型统一,支持socket,普通文件、块设备等
https://www.cnblogs.com/bigberg/p/8034629.html
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/606143882
https://www.zhihu.com/question/26943558
https://www.zhihu.com/question/421584363